enzymatic gravimetric method of prosky|Measurement of Dietary Fiber: Which AOAC Official : Brand Two general types of methods have been developed for isolating and analyzing dietary fiber: enzymatic-gravimetric and enzymatic-chemical. The food components isolated vary . Resultado da W/Amaro Traduções Jurídicas & Juramentadas, Londrina. 312 likes. Serviços de tradução jurídica, juramentada e consultoria especializada em Inglês Jurídico com .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Escorts masculinos en República Dominicana. Encuentra ho.
Determination of Total, Soluble, and Insoluble Dietary Fiber in Foods—Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method, MES-TRIS Buffer: Collaborative Study. Sungsoo C Lee. , Leon Prosky. , Jonathan W De Vries. Journal of AOAC INTERNATIONAL, Volume 75, Issue 3, 1 May 1992, . A collaborative study was conducted to determine the total dietary fiber (TDF) content of food and food products, using a combination of enzymatic and gravimetric . Determination of total, soluble, and insoluble dietary fiber in foods: enzymatic-gravimetric method, MES-TRIS buffer: collaborative study. Sungsoo C. Lee, L. Prosky, . A broad range of AOAC Official Methods of AnalysisSM (OMA) have been developed and approved for the measurement of dietary fiber (DF) and DF components since .
Two general types of methods have been developed for isolating and analyzing dietary fiber: enzymatic-gravimetric and enzymatic-chemical. The food components isolated vary . Lee, S, Prosky, L & DeVries, J (1992) Determination of total, soluble, and insoluble dietary fiber in foods: Enzymatic-gravimetric method, MES-TRIS buffer: Collaborative study. . Enzymes employed had to meet specific activity requirements and be devoid of contaminating enzymes active on dietary fibre components. The method that evolved was AOAC Official Method 985.29 ‘Total Dietary Fiber in . A collaborative study was conducted to determine the insoluble dietary fiber (IDF), soluble dietary fiber (SDF), and total dietary fiber (TDF) content of food and food products by .
The two main approaches for the determination of dietary fibre (DF) in food and feedstuffs are the enzymatic- and nonenzymatic-gravimetric AOAC (Association of Official Analytical .
A broad range of AOAC Official Methods of AnalysisSM (OMA) have been developed and approved for the measurement of dietary fiber (DF) and DF components since the adoption of . A broad range of AOAC Official Methods of Analysis SM (OMA) have been developed and approved for the measurement of dietary fiber (DF) and DF components since the adoption of the Prosky method (OMA 985.29). OMA 985.29 and other OMA were developed to support the Trowell definition of DF. However, these methods do not measure DF as defined . Prosky L, Mugford DC, Okuma K. Determination of insoluble, soluble, and . . The enzymatic-gravimetric methods are considered the most suitable for routine analysis of dietary fibers, but are . In 2007, McCleary described a method of extended enzymatic digestion at 37 degrees C to simulate human intestinal digestion followed by gravimetric isolation and quantitation of HMWDF and the use .
us to drop covid test requirement
Enzymatic–gravimetric methods have been recommended to determine dietary fiber. Recently in Brazil, the method 985.29 of AOAC (1990) was adopted for fiber levels notification on the label of packed food products (Brasil, 1998).Several problems as to the performance of these modifications of the method have been recorded (Jeraci and Van Soest, .
The precision attributes and use of the enzymatic-gravimetric method of Prosky et al. (1992) (AOAC 985.29) were evaluated using corn (BR 5202 Pampa) and oat (UFRGS 15) samples. The effect of laboratory batches carried out in different days were evaluated in six laboratory batches, using for each mat . OMA 2022.01 is a robust and reproducible method for the analysis of insoluble, soluble (SDFP and SDFS), and TDF in a wide range of matrixes. . Soluble, and Total Dietary Fiber in Foods Using a Rapid Integrated Procedure of Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatography: First Action 2022.01 J AOAC Int. 2022 Dec 22;106(1):127-145. doi: 10.1093 .ing to the enzymatic gravimetric Official Method of AnalysisSM (OMA) for total DF (TDF) [Prosky et al. (13); OMA 985.29] ( Figure 1)aswell as for insoluble DF (IDF) and soluble DF that .AOAC Official Method 2009.01 Total Dietary Fiber in Foods Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatographic Method First Action 2009 [Applicable to plant material, foods, and food ingredients consistent with CODEX Definition 2008 (ALINORM 09/32/26), including naturally occurring, isolated, modified, and synthetic polymers meeting that definition.]
The method that evolved was AOAC Official Method 985.29 ‘Total Dietary Fiber in Foods; Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method’ 4, 5. Subsequently, the method was extended to allow measurement of total, . Kansas, USA). Much higher DF values for FiberRite ® and Fibersym ® are obtained 39 using the Prosky TDF method (AOAC Method 985.29) 5. A fifth .
Of these type I methods, AACC International Approved Method 32-45.01 (AOAC method 2009.01) is the only procedure that measures all of the dietary fiber components as defined by Codex Alimentarius. The application of the Hellendoorn enzymatic-gravimetric method showed similar values of unavailable carbohydrate for both varieties; however, these values (21.6%) were higher than those previously reported for food grain legumes in the literature using the same method. The determination of soluble dietary fibre (SDF) yielded insignificant . Some known methods of extracting fiber from plant sources include dry processing, wet processing, chemical, gravimetric, enzymatic, physical, microbial or a combination of these methods.
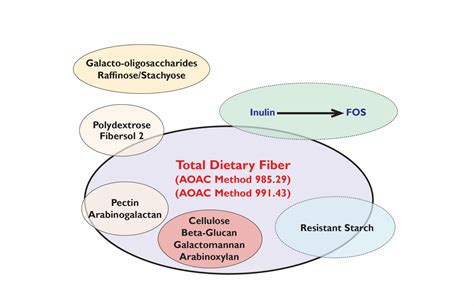
These methods are all enzymatic/gravimetric methods and the official status of each is summarised in Table 1 and acronyms are listed in Table 2. Figure 1. A schematic representation of the Prosky method (AOAC Method 985.29) for total dietary fiber determination. Concurrently, in the UK, Englyst and colleagues8,9), extendedThe enzymatic-gravimetric method of Prosky et al (1985), officially known as AOAC method 985.29 (AOAC 1990), has been adopted by government agencies in many countries for routine nutrient labeling analyses because it is simple and rather inexpensive. However, there is some concern that the values for
Main steps of the original and modified enzymatic-gravimetric AOAC methods AOAC original Prosky et al. (1988) AOAC modified Lee et al. (1992) Sample ~1 g Buffer Na-phosphate pH 6 MES/TRIS pH 8.2 Enzyme step 1 Termamyl 100°C, 15-30 min Termamyl 95-100°C, 35 min pH adjustment pH 7.5 Enzyme step 2 Protease 60°C, 30 min Protease 60°C, 30 minAOAC OFFICIAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS Supplement March 1995 32.1.17 AOAC Official Method 991.43 Total, Soluble, and Insoluble Dietary Fiber in Foods Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method, MES—TRIS Buffer First Action 1991 Final Action 1994 (Applicable to processed foods, grain and cereal products, fruits, and vegetables.) Method Performance:
Lee, S, Prosky, L & DeVries, J (1992) Determination of total, soluble, and insoluble dietary fiber in foods: Enzymatic-gravimetric method, MES-TRIS buffer: Collaborative study. Journal of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists 75, 395 – 416.Google Scholar An enzymatic-gravimetric method for determination of total dietary fiber in foods, in which soluble fiber and insoluble fiber are determined separately, was adopted first action by AOAC International. A collaborative study was conducted on an enzymatic-gravimetric method for determination of total dietary fiber in foods, in which soluble fiber and insoluble fiber are . Enzymatic gravimetric method: Prosky et al. (1988) Elleuch et al. (2008) Mango dietary fibre concentrate: 28.05: Enzymatic gravimetric method: Prosky et al. (1985) Vergara-Valencia et al. (2007) Nori algae: 34.7: Enzymatic gravimetric method: Prosky et al. (1988) Lahaye (1991) Arame algae: 74.6: Enzymatic gravimetric method: Prosky et al. (1988 .
Leon Prosky, Nils-Georg Asp, Ivan Furda, Jonathan W . (TDF) content of food and food products, using a combination of enzymatic and gravimetric procedures. The method was basically the same as published earlier (/. . each sample contained only about 1% TDF. The enzymatic-gravimetric method for determining TDF has been adopted official first .a method of extended enzymatic digestion at 37 C . following an international survey by Prosky et al. (6) in the . compounds are quantified by the AOAC gravimetric analytical method for .These methods are all enzymatic/gravimetric methods and the official status of each is summarised in Table 1 and acronyms are listed in Table 2. Figure 1. A schematic representation of the Prosky method (AOAC Method 985.29) for total dietary fiber determination. Concurrently, in the UK, Englyst and colleagues8,9), extended
A simplified enzymatic-gravimetric method for total dietary fiber (TDF) determination has been published and used in the Food Composition Laboratory of the U.S. Department of Agriculture since 1988. THis method gives comparable results to AOAC Official Methods 985.29 and 991.43 but the AOAC methods use 100 degrees C (water bath) to gelatinize .A collaborative study was conducted to determine the total dietary fiber (TDF) content of food and food products, using a combination of enzymatic and gravimetric procedures. The method was basically the same as published earlier (J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. (1984) 67, 1044-1052), with changes in the .
2.1 First Definition and Enzymatic Methods. In the middle of the twentieth century, the “dietary fiber” concept was first mentioned by Hipsley when he found a correlation between the lack of DF and pregnancy toxemia.The compounds included in Hipsley’s concept included lignin, cellulose and the hemicelluloses, defined as a non-digestible group of compounds that form . In 1985 the Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) adopted an enzymatic-gravimetric method, in which samples are subjected to serial digestion with amylase, amyloglucosidase, and protease, followed by isolation and gravimetric measurement of the residue as fiber (EGF). This method was first accepted in 1994 by the U.S. Food and Drug .
The application of the Hellendoorn enzymatic-gravimetric method showed similar values of unavailable carbohydrate for both varieties; however, these values (21.6%) were higher than those previously reported for food grain legumes in the literature using the same method.
us to drop covid test requirement for travel
Methods for analysis of dietary fibre
26 de jun. de 2023 · Play Make it Meme for free online now on Poki. Poki has the best free online games that you can play without the need of downloads or login. Join 30 million .
enzymatic gravimetric method of prosky|Measurement of Dietary Fiber: Which AOAC Official